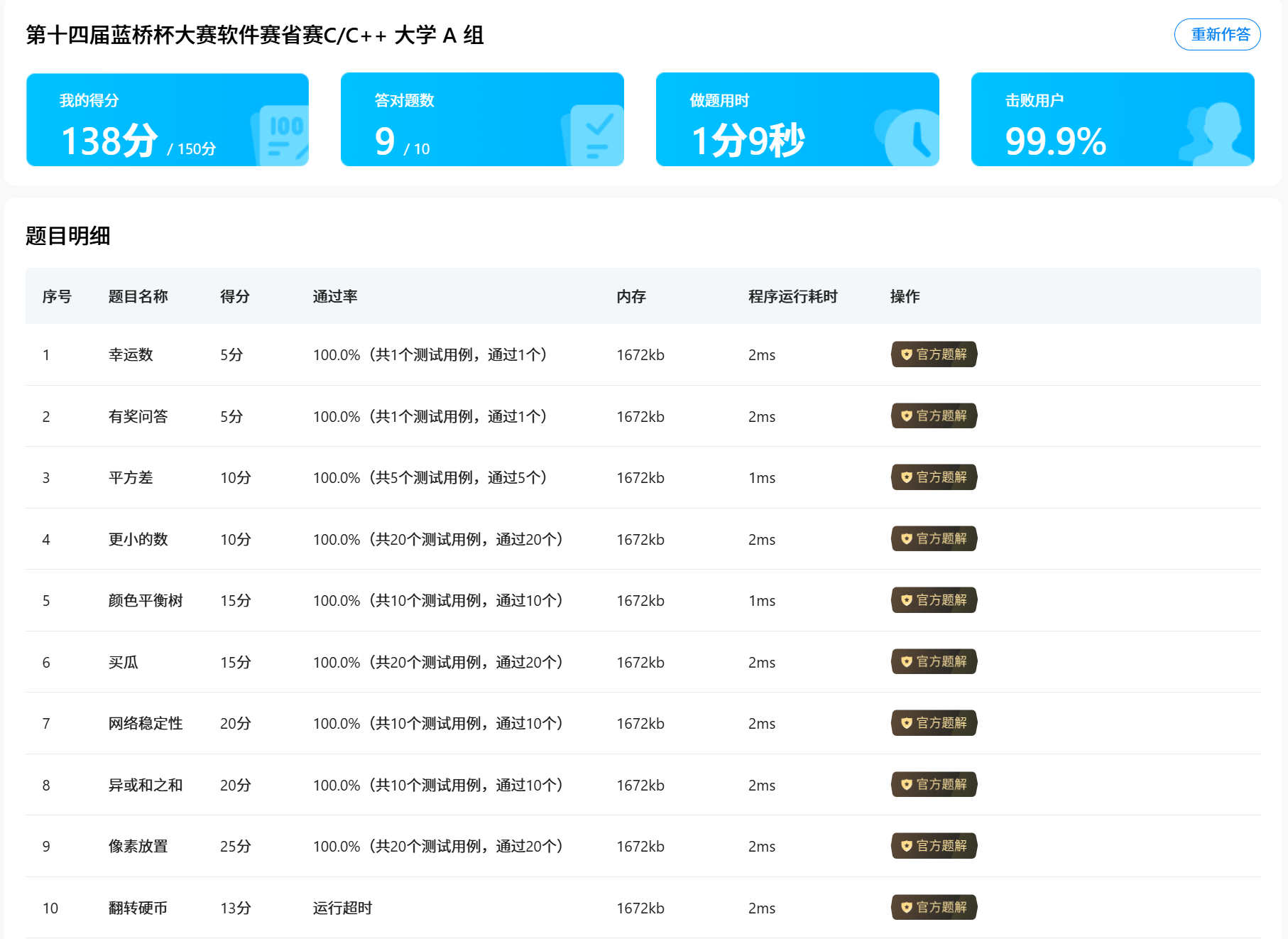
第十四届蓝桥杯软件赛省赛C++ A组 题解。
以下代码均通过测试,可放心食用。
本期知识点:DFS,DFS,DFS,高精度,Kruskal 重构树,LCA,树上倍增。
填空题 1. 幸运数(5分) 直接枚举 1-100000000 ,统计符合题意的个数。输出 4430091 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= 100000000 ; i++){ string num = to_string (i); if (num.size () & 1 ) continue ; int l = num.size () >> 1 ; int pre = 0 , suf = 0 ; for (int j = 0 ; j < l; j++){ pre += num[j] - '0' ; } for (int j = l; j < l + l; j++){ suf += num[j] - '0' ; } res += pre == suf; } cout << res; } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
2. 有奖问答(5分) 每个题 3 种情况:回答正确,回答错误,停止回答。
n 较小,$O(3^n)$ ,dfs 可以完成。输出 8335366 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int ed = 30 ; auto dfs = [&](auto &&self, int cur, int score) -> int { if (cur == ed) return score == 70 ; if (score == 100 ) return 0 ; int res = 0 ; res += self (self, cur + 1 , score + 10 ); res += self (self, cur + 1 , 0 ); res += score == 70 ; return res; }; cout << dfs (dfs, 0 , 0 ); } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
还可以 dp 完成,用 dp[i][j] 表示答到第 i 题时,得分为 10j 的情况数。
每次答题直接按题意转移即可,时间复杂度 $O(n)$。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () vector<array<int , 11>>dp (31 ); dp[0 ][0 ] = 1 ; int res = 0 ; for (int i = 1 ; i <= 30 ; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= 10 ; j++){ dp[i][j] += dp[i - 1 ][j - 1 ]; } for (int j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j++){ dp[i][0 ] += dp[i - 1 ][j]; } res += dp[i][7 ]; } cout << res; } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
程序题 3. 平方差(10分) 高精度模板题。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;class bigint {public : string n; bool f; bigint (string x, bool f = 0 ){ if (x[0 ] == '-' ){ this ->f = !f; n = x.substr (1 ); } else { this ->f = f; n = x; } } void print () if (f) cout << '-' ; cout << n; } bigint operator + (const bigint &o){ if (f == o.f) return bigint (add (n, o.n), f); if (f){ if (compare (n, o.n)) return bigint (sub (n, o.n), 1 ); return bigint (sub (o.n, n), 0 ); } if (compare (n, o.n)) return bigint (sub (n, o.n), 0 ); return bigint (sub (o.n, n), 1 ); } bigint operator - (const bigint &o){ return *this + bigint (o.n, !o.f); } bigint operator * (const bigint &o){ return bigint (mul (n, o.n), f ^ o.f); } private : bool compare (string a, string b) if (a.size () != b.size ()) return a.size () > b.size (); return a >= b; } string add (string a, string b) { string res; int carry = 0 ; int i = a.size () - 1 ; int j = b.size () - 1 ; while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || carry){ int sum = carry; if (i >= 0 ) sum += a[i--] - '0' ; if (j >= 0 ) sum += b[j--] - '0' ; carry = sum / 10 ; res += sum % 10 + '0' ; } reverse (res.begin (), res.end ()); return res; } string sub (string a, string b) { string res; int borrow = 0 ; int i = a.size () - 1 ; int j = b.size () - 1 ; while (i >= 0 ){ int diff = a[i--] - '0' - borrow; if (j >= 0 ) diff -= b[j--] - '0' ; borrow = diff < 0 ; diff += (diff < 0 ) * 10 ; res += diff + '0' ; } reverse (res.begin (), res.end ()); res.erase (0 , res.find_first_not_of ('0' )); if (res.empty ()) res = "0" ; return res; } string mul (string a, string b) { if (a == "0" || b == "0" ) return "0" ; reverse (a.begin (), a.end ()); reverse (b.begin (), b.end ()); string res (a.size() + b.size(), '0' ) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < a.size (); i++){ for (int j = 0 ; j < b.size (); j++){ int sum = (a[i] - '0' ) * (b[j] - '0' ) + (res[i + j] - '0' ); res[i + j] = sum % 10 + '0' ; res[i + j + 1 ] += sum / 10 ; } } reverse (res.begin (), res.end ()); res.erase (0 , res.find_first_not_of ('0' )); return res; } }; void solve () string a, b; cin >> a >> b; bigint A (a) , B (b) ; bigint res = A * A - B * B; res.print (); } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
4. 更小的数(10分) 枚举方式是这题的难点,这里应该枚举子段翻转的转轴位置。
从转轴中心往两边探索,如果遇到左侧大于右侧,那么翻转不满足。
如果遇到右侧大于左侧,翻转满足,
如果遇到左侧与右侧相同,那么能否翻转与这一位无关,延续先前的状态。
这样,时间复杂度是 $O(n^2)$。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () string s; cin >> s; int n = s.size (); int res = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++){ bool ok = 0 ; for (int l = i, r = i; l >= 0 && r < n; l--, r++){ if (s[l] < s[r]) ok = 0 ; if (s[l] > s[r]) ok = 1 ; res += ok; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++){ bool ok = 0 ; for (int l = i, r = i + 1 ; l >= 0 && r < n; l--, r++){ if (s[l] < s[r]) ok = 0 ; if (s[l] > s[r]) ok = 1 ; res += ok; } } cout << res; } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
5. 颜色平衡树(15分) 启发式合并,每次将合并两个节点时,总是将较小的树合并到较大的树上,以降低时间复杂度。
这里用 col 数组维护子树的 <颜色, 个数> 键值对,
用 num 数组维护子树的 <key, 有几个个数为key的颜色> 键值对。
当 num 中只有一个键值对时,说明所有颜色个数相同,计数。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int n; cin >> n; vector<vector<int >>adj (n + 1 ); vector<map<int , int >>col (n + 1 ), num (n + 1 ); for (int i = 1 ;i <= n; i++){ int c, fa; cin >> c >> fa; adj[fa].emplace_back (i); col[i][c]++; num[i][1 ]++; } int res = 0 ; auto dfs = [&](auto &&self, int u) -> void { for (auto &v : adj[u]){ self (self, v); if (col[u].size () < col[v].size ()){ swap (col[u], col[v]); swap (num[u], num[v]); } for (auto &[v_col, v_num] : col[v]){ if (col[u].count (v_col)){ int u_num = col[u][v_col]; num[u][u_num]--; if (num[u][u_num] == 0 ) num[u].erase (u_num); num[u][u_num + v_num]++; } else { num[u][v_num]++; } col[u][v_col] += v_num; } col[v].clear (); num[v].clear (); } if (num[u].size () == 1 ) res ++; }; dfs (dfs, 1 ); cout << res; } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
6. 买瓜(15分) dfs,但 $3^{30}$ 太大,需要充分的优化、剪枝。
为了更容易得到最少切数,应当将数组从大到小排序。
总和已经大于 m 时剪枝。
当前总和加上剩余所有数的和(维护后缀和)都小于 m 时剪枝。
当前切数已经大于最小切数时剪枝。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int n, m; cin >> n >> m; m <<= 1 ; vector<int >a (n), suf (n); for (auto &i : a) cin >> i, i <<= 1 ; sort (a.begin (), a.end (), greater<>()); suf[n - 1 ] = a[n - 1 ]; for (int i = n - 2 ; i >= 0 ; i--) suf[i] = suf[i + 1 ] + a[i]; int res = 66 ; auto dfs = [&](auto &&self, int cur, int sum, int cnt) -> void { if (sum == m) { res = min (res, cnt); return ; } if (cur == n || sum > m || sum + suf[cur] < m || cnt >= res) return ; self (self, cur + 1 , sum + a[cur], cnt); self (self, cur + 1 , sum + a[cur] / 2 , cnt + 1 ); self (self, cur + 1 , sum, cnt); }; dfs (dfs, 0 , 0 , 0 ); cout << (res == 66 ? -1 : res); } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
7. 网络稳定性(20分) 思路一:
求两个点间所有路径最小边权中的最大值
发现上述规律后,直接构建 Kruskal 重构树并处理 LCA 即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;struct edge { int u, v, w; }; void solve () int n, m, q; cin >> n >> m >> q; vector<edge>e (m); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){ int u, v, w; cin >> u >> v >> w; e[i] = {u, v, w}; } sort (e.begin (), e.end (), [](const edge &a, const edge &b){ return a.w > b.w; }); vector<int >p (2 * n); for (int i = 1 ; i < 2 * n; i++) p[i] = i; function<int (int )> find = [&](int x) { return x == p[x] ? x : p[x] = find (p[x]); }; vector<vector<int >>adj (2 * n); vector<int >val (2 * n); int idx = n; auto Kruskal = [&](){ for (auto &[u, v, w] : e){ int pu = find (u), pv = find (v); if (pu == pv) continue ; val[++idx] = w; adj[idx].emplace_back (pu); adj[idx].emplace_back (pv); p[pu] = p[pv] = idx; } }; Kruskal (); vector<int >dep (idx + 1 ); constexpr int M = 20 ; vector<array<int , M>>f (idx + 1 ); function<void (int )> dfs = [&](int u){ for (auto &v : adj[u]){ dep[v] = dep[u] + 1 ; f[v][0 ] = u; for (int i = 1 ; i < M; i++) f[v][i] = f[f[v][i - 1 ]][i - 1 ]; dfs (v); } }; for (int i = 1 ; i <= idx; i++) if (find (i) == i) dfs (i); auto lca = [&](int x, int y) -> int { if (dep[x] < dep[y]) swap (x, y); for (int i = M - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (dep[f[x][i]] >= dep[y]) x = f[x][i]; for (int i = M - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (f[x][i] != f[y][i]) x = f[x][i], y = f[y][i]; return f[x][0 ]; }; while (q--){ int x, y; cin >> x >> y; if (find (x) != find (y)) cout << -1 << '\n' ; else cout << val[lca (x, y)] << '\n' ; } } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
思路二:
建立最大生成树后,考虑使用 lca + 倍增维护到祖先的最小边权。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;struct edge { int u, v, w; }; void solve () int n, m, q; cin >> n >> m >> q; vector<edge>e (m); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; i++){ cin >> e[i].u >> e[i].v >> e[i].w; } sort (e.begin (), e.end (), [](const edge& a, const edge& b){ return a.w > b.w; }); vector<int >p (n + 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) p[i] = i; function<int (int )> find = [&](int x){ return x == p[x] ? x : p[x] = find (p[x]); }; vector<vector<pair<int , int >>>adj (n + 1 ); for (auto &[u, v, w] : e){ int fu = find (u), fv = find (v); if (fu == fv) continue ; p[fu] = fv; adj[u].emplace_back (v, w); adj[v].emplace_back (u, w); } constexpr int M = 20 ; vector<int >dep (n + 1 ); vector<vector<int >>f (n + 1 , vector <int >(M)); vector<vector<int >>cost (n + 1 , vector <int >(M)); function<void (int , int )> dfs = [&](int u, int fa){ for (auto &[v, w] : adj[u]){ if (v == fa) continue ; dep[v] = dep[u] + 1 ; f[v][0 ] = u; cost[v][0 ] = w; for (int i = 1 ; i < M; i++){ f[v][i] = f[f[v][i - 1 ]][i - 1 ]; cost[v][i] = min (cost[v][i - 1 ], cost[f[v][i - 1 ]][i - 1 ]); } dfs (v, u); } }; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++) if (i == find (i)) dep[i] = 1 , dfs (i, 0 ); auto lca = [&](int x, int y) -> int { if (dep[x] < dep[y]) swap (x, y); for (int i = M - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (dep[f[x][i]] >= dep[y]) x = f[x][i]; if (x == y) return x; for (int i = M - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (f[x][i] != f[y][i]) x = f[x][i], y = f[y][i]; return f[x][0 ]; }; auto min_path = [&](int x, int y) -> int { int res = 1e18 ; for (int i = M - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) if (dep[f[x][i]] >= dep[y]) res = min (res, cost[x][i]), x = f[x][i]; return res; }; while (q--){ int x, y; cin >> x >> y; if (find (x) != find (y)){ cout << -1 << '\n' ; continue ; } int fa = lca (x, y); cout << min (min_path (x, fa), min_path (y, fa)) << '\n' ; } } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
8. 异或和之和(20分) 对每一个元素,尝试计算以该元素为结尾的所有字段的异或和之和。
计数每一位出现的次数 cnt[j] ,当此数第 j 位为 0 时,每一位出现次数均不变。
当次数第 j 位为 1 时,该位出现次数变为 i - cnt[j],再统计贡献即可。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int n; cin >> n; int res = 0 ; vector<int >cnt (21 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ int a; cin >> a; for (int j = 0 ; j <= 20 ; j++){ if (a >> j & 1 ) cnt[j] = i - cnt[j]; res += (1 << j) * cnt[j]; } } cout << res; } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
9. 像素放置(25分) dfs,填入后 check 所有被这个点的填入所确定的数字,递归该过程。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int n, m; cin >> n >> m; vector<vector<char >>a (n + 2 , vector <char >(m + 2 )); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++){ cin >> a[i][j]; } } vector<vector<bool >>vis (n + 2 , vector <bool >(m + 2 )); auto check = [&](int x, int y) -> bool { if (a[x][y] == '_' ) return 1 ; int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = x - 1 ; i <= x + 1 ; i++){ for (int j = y - 1 ; j <= y + 1 ; j++){ cnt += vis[i][j]; } } return cnt == a[x][y] - '0' ; }; function<void (int , int )>dfs = [&](int x, int y){ int ok = 1 ; vis[x][y] = 1 ; if (x - 1 >= 1 && y - 1 >= 1 ){ ok &= check (x - 1 , y - 1 ); } if (y == m && x - 1 >= 1 ){ ok &= check (x - 1 , y); } if (x == n && y - 1 >= 1 ){ ok &= check (x, y - 1 ); } if (x == n && y == m){ ok &= check (x, y); } if (ok) { if (x == n && y == m){ for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++){ cout << vis[i][j]; } cout << '\n' ; } exit (0 ); } if (y == m) dfs (x + 1 , 1 ); else dfs (x, y + 1 ); } vis[x][y] = 0 ; ok = 1 ; if (x - 1 >= 1 && y - 1 >= 1 ){ ok &= check (x - 1 , y - 1 ); } if (y == m && x - 1 >= 1 ){ ok &= check (x - 1 , y); } if (x == n && y - 1 >= 1 ){ ok &= check (x, y - 1 ); } if (x == n && y == m){ ok &= check (x, y); } if (ok) { if (x == n && y == m){ for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ for (int j = 1 ; j <= m; j++){ cout << vis[i][j]; } cout << '\n' ; } exit (0 ); } if (y == m) dfs (x + 1 , 1 ); else dfs (x, y + 1 ); } }; dfs (1 , 1 ); } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
10. 翻转硬币(13/25分) 正解疑似太难,学不会)这里给出一个暴力的解法,能通过 55%
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 #include <bits/stdc++.h> #define int long long using namespace std;void solve () int n; cin >> n; int cnt = 1 ; vector<bool >a (n + 1 ); a[1 ] = true ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++){ if (a[i]) continue ; a[i] = true ; cnt++; for (int j = i * 2 ; j <= n; j += i){ a[j] = !a[j]; } } cout << cnt; } signed main () ios::sync_with_stdio (0 ); cin.tie (0 ); solve (); return 0 ; }
至于正解,把解析搬过来供大家欣赏。